MPLS Questions
Question 1
What is a reason for 6PE to use two MPLS labels in the data plane instead of one?
A. 6PE allows penultimate hop popping and has a requirement that all P routers do not have to be IPv6 aware.
B. 6PE does not allow penultimate hop popping.
C. It allows MPLS traffic engineering to work in a 6PE network.
D. It allows 6PE to work in an MPLS network where 6VPE is also deployed.
Answer: A
Question 2
For which kind of MPLS deployment is the next-hop-self all keyword used on a BGP neighbor command?
A. 6VPE
B. MPLS Carrier’s carrier
C. inter-AS MPLS VPN option D
D. inter-AS MPLS VPN option C
E. Unified MPLS
Answer: E
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit.

Which statement is true?
A. This is an MPLS TE point-to-multipoint LSP in an MPLS network.
B. This is an MPLS TE multipoint-to-point LSP in an MPLS network.
C. This is a point-to-multipoint LSP in an MPLS network.
D. This is a multipoint-to-multipoint LSP in an MPLS network.
Answer: D
Question 4
A service provider is deploying L2VPN LAN services in its MPLS cloud. Which statement is true regarding LDP signaling and autodiscovery?
A. LDP signaling requires that each PE is identified, and that an LDP session is active with its P neighbor for autodiscovery to take place.
B. LDP signaling requires that each P is identified, and that a targeted LDP session is active for autodiscovery to take place.
C. LDP signaling requires that each PE is identified, and that a targeted LDP session with a BGP route reflector is active for autodiscovery to take place. j D. LDP signaling requires that each PE is identified, and that a targeted LDP session is active for autodiscovery to take place.
Answer: D
Question 5
Which two mechanisms can be used to eliminate Cisco Express Forwarding polarization? (Choose two)
A. alternating cost links
B. the unique-ID/universal-ID algorithm
C. Cisco Express Forwarding antipolarization
D. different hashing inputs at each layer of the network
Answer: B D
Question 6
Service provider SP 1 is running the MPLS-VPN service. The MPLS core network has MP-BGP configured with RR-1 as route reflector. What will be the effect on traffic between PE1 and PE2 if router P1 goes down?
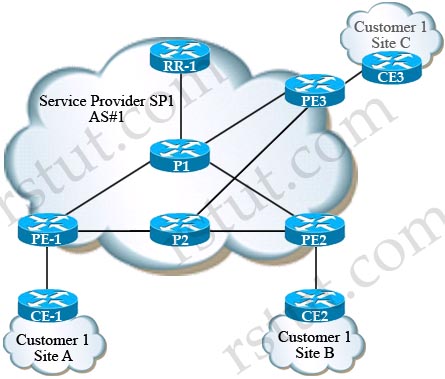
A. No effect, because all traffic between PE1 and PE2 will be rerouted through P2.
B. No effect, because P1 was not the only P router in the forwarding path of traffic.
C. No effect, because RR-1 will find an alternative path for MP-BGP sessions to PE-1 and PE-2.
D. All traffic will be lost because RR-1 will lose the MP-BGP sessions to PE-1 and PE-2.
Answer: D
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit.

Which statement is true?
A. R1 routes this pseudowire over MPLS TE tunnel 1 with transport label 20.
B. The default route 0.0.0.0/0 is available in the IPv4 routing table.
C. R1 is using an MPLS TE tunnel for this pseudowire, because the IP path is not available.
D. R1 has preferred-path configured for the pseudowire.
Answer: D
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit.
| CE1#trace Protocol [ip]: ipv6 Target IPv6 address: 2001:db8:100:1::7 Source address: 2001:db8:100:1::5 Insert source routing header? [no]: Numeric display? [no]: Timeout in seconds [3]: Probe count [3]: Minimum Time to Live [1]: Maximum Time to Live [30]: Priority [0]: Port Number [0]: Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to 2001:10:100:1::7 1 2001:db8:1:5::1 1 msec 1 msec 1 msec 2 ::FFFF:10.1.2.4 [MPLS: Labels 17/23 Exp 0] 2 msec 2 msec 2 msec 3 2001:db8:1:7::2 [AS 1] [MPLS: Label 23 Exp 0] 2 msec 1 msec 1 msec 4 2001:db8:1:7::7 [AS 1] 2 msec 1 msec 2 msec |
Which statement is true?
A. There is an MPLS network that is running 6PE, and the ingress PE router has no mpls ip propagate-ttl.
B. There is an MPLS network that is running 6VPE, and the ingress PE router has no mpls ip propagate-ttl.
C. There is an MPLS network that is running 6PE or 6VPE, and the ingress PE router has mpls ip propagate-ttl.
D. There is an MPLS network that is running 6PE, and the ingress PE router has mpls ip propagate-ttl.
E. There is an MPLS network that is running 6VPE, and the ingress PE router has mpls ip propagate-ttl.
Answer: C
Question 9
Which statement is true comparing L2TPv3 to EoMPLS?
A. L2TPv3 requires OSPF routing, whereas EoMPLS does not.
B. EoMPLS requires BGP routing, whereas L2TPv3 does not.
C. L2TPv3 carries L2 frames inside MPLS tagged packets, whereas EoMPLS carries 12 frames inside IPv4 packets.
D. L2TPv3 carries L2 frames inside IPv4 packets, whereas EoMPLS carries L2 frames inside MPLS packets.
Answer: D
Question 10
What is a key advantage of Cisco GET VPN over DMVPN?
A. Cisco GET VPN provides zero-touch deployment of IPSEC VPNs.
B. Cisco GET VPN supports certificate authentication for tunnel establishment.
C. Cisco GET VPN has a better anti-replay mechanism.
D. Cisco GET VPN does not require a secondary overlay routing infrastructure.
Answer: D

Q5 – If C was anti-polarization weight, this choice was true too.
Question 7:
please a short explanation!
Q7. Short Explanation please 🙂
how many questions there are to study ?
For MPLS protection and restoration mechanisms, check the below article series…
http://ipcisco.com/mpls-protection-and-restoration-part-4-local-protection-fast-reroute/
Q3. Is it not point to multipoint MPLS TE ? rstut any explanation ?