BGP Questions
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit.

Which statement is true?
A. BGP peer 10.1.2.3 is performing inbound filtering.
B. BGP peer 10.1.2.3 is a route reflector.
C. R1 is a route reflector, but BGP peer 10.1.2.3 is not a route reflector client.
D. R1 still needs to send an update to the BGP peer 10.1.2.3.
Answer: D
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit.
| BGP(0): 10.1.3.4 rcvd UPDATE w/ attr: nexthop 10.1.3.4, origin i, metric 0/ merged path 4, AS PATH BGP(0): 10.1.3.4 rcvd 10.100.1.1/32…duplicate ignored |
Notice that debug ip bgp updates has been enabled. What can you conclude from the debug output?
A. This is the result of the clear ip bgp 10.1.3.4 in command.
B. This is the result of the clear ip bgp 10.1.3.4 out command.
C. BGP neighbor 10.1.3.4 performed a graceful restart.
D. BGP neighbor 10.1.3.4 established a new BGP session.
Answer: A
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit.

Which command is configured on this router?
A. bgp update-delay 60
B. neighbor 10.100.1.1 maximum-prefix 200
C. neighbor 10.100.1.1 maximum-path 2
D. neighbor 10.100.1.1 ebgp-multihop 2
Answer: B
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit.

What is a reason for the RIB-failure?
A. CEF is not enabled on this router.
B. The route 10.100.1.1/32 is in the routing table, but not as a BGP route.
C. The routing table has yet to be updated with the BGP route.
D. The BGP route is filtered inbound and hence is not installed in the routing table.
Answer: B
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit.
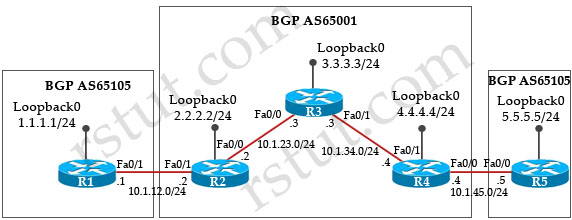

Why is R2 unable to ping the loopback interface of R4?
A. The local preference is too high.
B. The weight is too low.
C. The next hop is not reachable from R2.
D. The route originated from within the same AS.
Answer: C
Question 6
Refer to the exhibit.

Why is network 172.16.1.0/24 not installed in the routing table?
A. There is no ARP entry for 192.168.1.1.
B. The router cannot ping 192.168.1.1.
C. The neighbor 192.168.1.1 just timed out and BGP will flush this prefix the next time that the BGP scanner runs.
D. There is no route for 192.168.1.1 in the routing table.
Answer: D
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit.

Which two statements are true? (Choose two)
A. This router is not 4-byte autonomous system aware.
B. This router is 4-byte autonomous system aware.
C. The prefix 10.100.1.1/32 was learned through an autonomous system number with a length of 4 bytes, and this router is 4-byte autonomous system aware.
D. The prefix 10.100.1.1/32 was learned through an autonomous system number with a length of 4 bytes, and this router is not 4-byte autonomous system aware.
E. The prefix 10.100.1.1/32 was originated from a 4-byte autonomous system.
Answer: A D
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit.
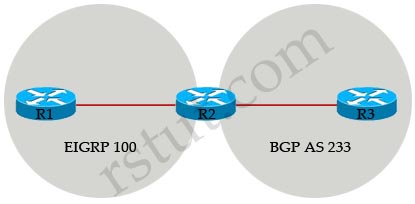
R2 is mutually redistributing between EIGRP and BGP.
Which configuration is necessary to enable R1 to see routes from R3?
A. The R3 configuration must include ebgp-multihop to the neighbor statement for R2.
B. The R2 BGP configuration must include bgp redistribute-intemal.
C. R1 must be configured with next-hop-self for the neighbor going to R2.
D. The AS numbers configured on R1 and R2 must match.
Answer: B
Question 9
Which group of neighbors can be configured as a BGP peer group?
A. a group of iBGP neighbors that have the same outbound route policies
B. a group of iBGP and eBGP neighbors that have the same inbound distribute-list
C. a group of eBGP neighbors in the same autonomous system that have different outbound route policies
D. a group of iBGP neighbors that have different outbound route policies
Answer: A
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit.
| *May20 12:16: BGP(4):10.1.1.2 rcvd UPDATE w/ attr:nexthop 10.1.1.2,origin ?, localpref 100,metric 0,extended community RT:999:999 *May20 12:16: BGP(4):10.1.1.2 rcvd 999:999:192.168.1.99/32,label 29—DENIED due to:extended community not supported |
You have just created a new VRF on PE3. You have enabled debug ip bgp vpnv4 unicast updates on PE1, and you can see the route in the debug, but not in the BGP VPNv4 table. Which two statements are true? (Choose two)
A. VPNv4 is not configured between PE1 and PE3.
B. address-family ipw4 vrf is not configured on PE3.
C. After you configure route-target import 999:999 for a VRF on PE3, the route will be accepted.
D. PE1 will reject the route due to automatic route filtering.
E. After you configure route-target import 999:999 for a VRF on PE1, the route will be accepted.
Answer: D E

Somebody can explain question number 5.
Not question number 5 please 7.
I’m also confused with the answer to Q5. Is it that the next-hop is unreachable from R2 or OR, R2 completely doesn’t know the next-hop to route 4.4.4.0/24, highlighted by the fact that it doesn’t have > next to the route!!!!
Somebody can explain question number 1 please!
@Nick routing table version (Tbl Ver) for 10.1.2.3 is 1, other routers have version 2, so it should be updated
Q3
Router_B# show ip bgp summary
BGP router identifier 10.0.0.2, local AS number 300
BGP table version is 87, main routing table version 87
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
10.0.0.1 4 200 965 948 0 0 0 00:02:24 Idle (PfxCt)
Router_B# show ip bgp neighbors 10.0.0.1
BGP neighbor is 10.0.0.1, remote AS 200, external link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 0.0.0.0
BGP state = Idle
Last read 00:02:43, hold time is 180, keepalive interval is 60 seconds
Received 965 messages, 0 notifications, 0 in queue
Sent 948 messages, 2 notifications, 0 in queue
Default minimum time between advertisement runs is 30 seconds
For address family: IPv4 Unicast
BGP table version 87, neighbor version 0
Index 1, Offset 0, Mask 0x2
Route refresh request: received 0, sent 0, maximum limit 10
Threshold for warning message 80%
Connections established 2; dropped 2
Last reset 00:02:43, due to BGP Notification sent, update malformed
Message received that caused BGP to send a Notification:
FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF
00600200 00001940 01010040 02040201
00C84003 040A0000 01800404 00000000
180A0001 180A0002 180A0003 180A0004
180A0005 180A0006 180A0007 180A0008
180A0009 180A000A 180A000B 180A000C
Peer had exceeded the max. no. of prefixes configured.
Reduce the no. of prefix and clear ip bgp 10.0.0.1 to restore peering
External BGP neighbor can be up to 2 hops away.
No active TCP connection
Note: Use this command in order to restore the peer ability:
Router_B# clear ip bgp 10.0.0.1
Q4
Q. What does r RIB-Failure mean in the show ip bgp command output?
R1> show ip bgp
BGP table version is 5, local router ID is 200.200.200.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i – internal,
r RIB-failure
Origin codes: i – IGP, e – EGP, ? – incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
r> 6.6.6.0/24 10.10.13.3 0 130 0 30 i
*> 7.7.7.0/24 10.10.13.3 0 125 0 30 i
A. When BGP tries to install the bestpath prefix into Routing Information Base (RIB) (for example, the IP Routing table), RIB might reject the BGP route due to any of these reasons:
Route with better administrative distance already present in IGP. For example, if a static route already exists in IP Routing table.
Memory failure.
The number of routes in VPN routing/forwarding (VRF) exceeds the route-limit configured under the VRF instance.
In such cases, the prefixes that are rejected for these reasons are identified by r RIB Failure in the show ip bgp command output and are not advertised to the peers. This feature was first made available in Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(08.05)T.
Q5,
4.4.4.0 it is advertised by R4 but it is not the Best (>)and not installed becasue R2 does not have route to reach next-hop address of 10.1.1.4 ;
For BGP to mark rotues the best, next hop must be reachable; to fix it, use static route or advertise route in IGB or change next-hop IP via routing -map or use next-hop-self option/ feature;
Q5,
4.4.4.0 it is advertised by R4 but it is not the Best (>)and not installed becasue R2 does not have route to reach next-hop address of 10.1.34.4 ;
For BGP to mark rotues the best, next hop must be reachable; to fix it, use static route or advertise route in IGB or change next-hop IP via routing -map or use next-hop-self option/ feature;
Can any one explain Q1 for me?? thanks
Q3
Why choose B , Why not choose D
Q7:
A & D are the correct answer since:
This router is not 4-byte autonomous system aware. Since, if this router was a 4-byte AS, it would show the AS4 format (xx.yy) instead of “23456” in the network path.
Mason- Question 3 answer is as it is because of PfxCt shown.means you reached maximum prefix number allowed
Q3. All answers could be ok but from the output shown one stands out: in the prefix received there’s PfxCt and state is idle. Idle (PfxCt) – for prefix count over limit. It means that probably allowed prefix maximum number is configured and the number of prefixes received has reached such maximum number.
Q5 answer should be D
The output shown is about the BGP table (No RIB) so you dont know if 1.1.34.4 is reachable or not. Problem is R2, R3 and R4 are running iBGP, hence a route advertised from R4 to R3 wont be advertised to another iBGP Peer. You need a Full meshed network to accomplish that.
Question 2 is not B ?
The update is from 10.1.3.4 ,
clear ip bgp 10.1.3.4 in this works if you have soft-reconfiguration configured and still you will bot get that message as the router process the existing saved bgp updates from 10.1.3.4 so there is no retransmition involved.
If you don’t have soft reconfiguration configured it will drop the TCP session and remoev all updates so you will still not get that messate.
You’ll get that message if you do a clear ip bgp neighbor out, the neighbor beeing the BGP speaker connected to 10,1,3.4. In this case the updates will be retransmited and is possible to have duplicates like in the debug output.
Shahar…your explanation for Q7 is incorrect. 4 byte autonomous system aware doesn’t mean it follows the (xx.yy) format. This is the difference between asdot and ASplain notation. You can have 2 byte or 4 byte aware in the asdot notation. The reason the router is not 4-byte aware is because you see AS 23456 in the path. This is a special AS number ( created by RFC 4893) which is used for backwards compatibility between 4 byte aware and non 4 byte aware BGP speakers.
Sources:
cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/ios-nx-os-software/border-gateway-protocol-bgp/data_sheet_C78-521821.html
cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/iproute_bgp/configuration/xe-3s/irg-xe-3s-book/irg-4byte-asn.html
hii can anyone explan Q1 pls
Question 2, Butch is correct. Correct answer is B.
Way at bottom of the following link:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/border-gateway-protocol-bgp/11651-technote-table version-00.html
clear ip bgp out command
Can someone explain why q10 answers are D and E and not C and D ?