STP Questions
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit.
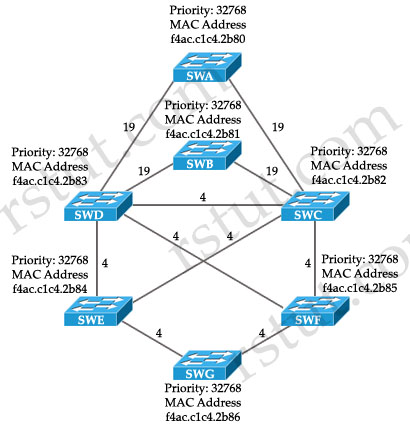
All switches have default bridge priorities, and originate BPDUs with MAC addresses as indicated. The numbers shown are STP link metrics. Which two ports are in blocking state after STP converges? (Choose two)
A. the port on switch SWD that connects to switch SWE
B. the port on switch SWF that connects to switch SWG
C. the port on switch SWD that connects to switch SWC
D. the port on switch SWB that connects to switch SWD
Answer: C D
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit.

All switches have default bridge priorities, and originate BPDUs with MAC addresses as indicated. The numbers shown are STP link metrics. Which two ports are forwarding traffic after STP converges? (Choose two)
A. The port connecting switch SWD with switch SWE
B. The port connecting switch SWG with switch SWF
C. The port connecting switch SWC with switch SWE
D. The port connecting switch SWB with switch SWC
Answer: C D
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit.

Which two statements about the output are true? (Choose two)
A. 802.1D spanning tree is being used.
B. Setting the priority of this switch to 0 for VLAN1 would cause it to become the new root.
C. The hello, Max-age, and forward delay timers are not set to their default values.
D. Spanning-tree PortFast is enabled on GigabitEthernet1/1.
Answer: A B
Question 4
Which statement is true regarding UDLD and STP timers?
A. The UDLD message timer should be two times the STP forward delay to prevent loops.
B. UDLD and STP are unrelated features, and there is no relation between the timers.
C. The timers need to be synced by using the spanning-tree udld-sync command.
D. The timers should be set in such a way that UDLD is detected before the STP forward delay expires.
Answer: D
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit.

Which technology does the use of bi-directional BPDUs on all ports in the topology support?
A. RSTP
B. MST
C. Bridge Assurance
D. Loop Guard
E. Root Guard
F. UDLD
Answer: C
Question 6
Refer to the exhibit.

Which two statements are true about the displayed STP state? (Choose two)
A. The STP version configured on the switch is IEEE 802.1w.
B. Port-channel 1 is flapping and the last flap occurred 1 minute and 17 seconds ago.
C. The switch does not have PortFast configured on Gi0/15.
D. BPDUs with the TCN bit set are transmitted over port channel 1.
Answer: C D
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit.

While troubleshooting high CPU utilization on one of your Cisco Catalyst switches, you find that the issue is due to excessive flooding that is caused by STP. What can you do to prevent this issue from happening again?
A. Disable STP completely on the switch.
B. Change the STP version to RSTP.
C. Configure PortFast on port-channel 1.
D. Configure UplinkFast on the switch.
E. Configure PortFast on interface Gi0/15.
Answer: E
Question 8
Which two statements are true about RSTP? (Choose two)
A. By default, RSTP uses a separate TCN BPDU when interoperating with 802.1D switches.
B. By default, RSTP does not use a separate TCN BPDU when interoperating with 802.1D switches.
C. If a designated port receives an inferior BPDU, it immediately triggers a reconfiguration.
D. By default, RSTP uses the topology change TC flag.
E. If a port receives a superior BPDU, it immediately replies with its own information, and no reconfiguration is triggered.
Answer: B D

hi Friends ..
can anyone explain Q3 please..
thanks
i think it’s wrong exhibit 😉
Can anyone explain q1? Why is the answer C and D instead of B and C?
Lasco; SWD has one of its port in blocking state making SWC the best path to the root bridge. And SWE and SWF have the a tie on priority and link cost SWG however ends up having the higher mac-add thus gets its port toward SWF blocked.
Explain q1 pls!
q1. only C? why B->D is BLK? It has lowest MAC..
q2. ACD?
Q1 is wrong, MAC is only used to decide Root, ties are defined by port prio.
Remember that it is the port that is blocked, not the link.
Since we have two equal cost paths, you need to know tie breaking rules in this scenario. Here they are,
1. Lowest Sending Bridge ID
2. Lowest Port Priority (of sender)
3. Lowest Interface number (of sender)
Bridge ID means Priority and MAC, so yes Q1 is correct we use the MAC address
Can anyone explain Question-1 and Question2 please
Neither port on segment SWD-SWB are Root Ports. . . Therefore, one must be a Designated Port. The superior BPDU for the segment will be the one with the lower MAC address. SWB has the lower MAC.
Therefore:
[SWD] (BL) ———————— (DP) [SWB]
Q1. D is NOT a correct answer.
Q1/– AC correct answers
Q1. =
C. the port on switch SWD that connects to switch SWC
D. the port on switch SWB that connects to switch SWD
Q2. =
A. The port connecting switch SWD with switch SWE
B. The port connecting switch SWG with switch SWF
It is very clear. You have to put attention in: “The port on switch SWx” and “The port connecting”…
Q3. =
Here the correct options:
Which two statements about the output are true? (Choose two)
A. 802.1D spanning tree is being used.
B. Setting the priority of this switch to 0 for VLAN1 would cause it to become the new root.
C. The hello, Max-age, and forward delay timers are not set to their default values.
D. Spanning-tree PortFast is enabled on GigabitEthernet1/1.
Answer: A B
Sorry, The answer of Q2 are “C D”. They are not asking about “blocking Ports, but, forwarding ports”…
I was also dismayed but Q
I was also dismayed buy Q1 and Q2 at first. I think the best practice when looking at these complicated switch architecture is to remember fundamentals: this is a scenario that wants you to demonstrate understanding of the Root switch and Root port election process. So, it’s best to start with where the root switch will be and work down from there. It’s setup nicely in both scenarios to do just that because the lowest MAC address switch starts at the top and then the lower priority/higher mac addresses move down the architecture. SWA wins the root election and of course all ports in SWA are forwarding. SWB introduces the possibility for a switching loop so it’s important to understand which ports will be put into the blocking state. Since SWD is a higher MAC address it will end up with a blocked port connected to SWB to prevent a loop: and this is one of the correct answers. To prevent the possibility of another potential switching loop, SWD again ends up with the higher MAC address so blocking the link between D and C prevents a B/C/D switching loop. For Q2, we know SWB to SWC are forwarding because we already identified the blocking port. So for the last correct answer in Q2 let’s consider what must be done to prevent a switch loop between SWC/SWD/SWE. SWE to SWD will be blocked because SWC has a lower MAC addres so it wins the forwarding port. And to look at it further, you could try to further understand what would happen with ports on SWG. Would the ports on SWG try to go through SWE or SWF? SWE has the lower MAC address so the port from SWG to SWE would win the forwarding election. Therefore, in Q2, answer B could never be correct. hth
Are these questions still valid?
Why is the answer on Q7 that you have to configure it as an Access port. Is it because it then will not participate in STP? Can someone verify if my thoughts are correct?
Question 1.
C,D is correct.
Draw a square A-C , A-D, B-C, B-D
The hello from to B-D is 38. The hello from D-B is 19. So SwB should be blocking and SwD is the DP.
For Q7).
Answer E is correct.
The high CPU utilisation is cause by excessive flooding for Topology change notifications.
You can see that Topology change 296 time for interface Gi0/15, it will send TCN every time.
If you enable PORTFAST on Gi0/15, the link flap on Gi0/15 will not send TCN. so the CPU utilisation will come down.
Guys,
Whoever is interested for ccie r&s study group, add me on the skype:ernesto.birneto
Why there are different answers in the forum? what we stick to? if you cannot make an explanation why you just say correct answers are so and so and not providing explanation dudes? this is misleading!!!
Q2:
The question says “The port connecting” In my opinion, doesn’t says nothing about which port connect to… if it’s D or E or sth..
A. The port connecting switch SWD with switch SWE
—> Port D is DP and port E is BLK: This is not correct.
B. The port connecting switch SWG with switch SWF
—> Port G is BLK and Port F is DP: This is not correct.
C. The port connecting switch SWC with switch SWE
—> Port C is DP and port E is ROOT Port: Both are in Fordwarding state so is Correct.
D. The port connecting switch SWB with switch SWC
—> Port B is ROOT Port and Port C is DP: Both are in Fordwarding state so is Correct
So for me, the correct is C,D.
It’s different Q2 and Q1 so in Q1 the question says the port “the port on switch SWD…” .
For Q1 and Q2 we need to look first which switch will be the root bridge, then look if which from the other switches will be the root port, then for network segments that doesn’t have the root port, need to determine which of the ports will be the designated and non-designated ports
Again the steps for selecting the Spanning Tree Designated Port are:
1) Select the port on the Switch on the network segment (which does not include a Root Port) with the lowest accumulated Spanning Tree Path Cost to the Spanning Root Bridge (Root Switch) as the Designated Port and other side of the Designated Port will be the Non-Designated Port.
2) If there is a tie in accumulated Path Costs between the two switches in the network segment, then select the port on the switch with the lowest Spanning Tree Switch ID as the Designated Port and other side of the Designated Port as the Non-Designated Port.
Hello R&S Tut please correct question number 3.
Could anyone explain Q6 ?
Why D is correct? I think, MST does not use TCN BPDU….
This is a great forum! Could anyone tell me what combination of materials would be needed to successfully pass the CCIE written exam?
Thanks
q1
On link B/D B will block as link B/C is root port, C has lower mac than D.
But on the link B/D, D will be designated port for that segment as it is closer to the route bridge than B.
Is that right?
Q1
Link D/C both D & C have same distance to route so lowest mac on this segment determines who is blocking and who is designated. In this case C has lower mac so becomes designated
Is that right?
I think question 2 answer should be A and C
Could anyone kindly upload / share the latest dump over any file sharing site and share the link? It would be tough to email dumps every time. 😉
2 CiscoKid:
That is right. It is #3 from below:
A BPDU is superior than another if it has:
1. a lower root bridge ID;
2. a lower path cost to the root;
3. a lower sending bridge ID;
4. a lower sending port ID.
2 CiscoKid:
P.S. The above explanation was regarding the D/C link. For the B/D link it would be #2, you are totally correct.
Q2. Answer is A, C kindly check and confirm, and D is wro ng because SwB is Root Port so it cannot forward frames.
Young man, all root port are in the forwarding state…
If anyone wants to know how the exhibit in Q1 and Q2 looks after STP stabilizes here’s the link:
http://www.netdaily.org/tag/ccie-stp-exhibit/
@Ryoji. Question 6 Regarding answer D, output suggests that Port-channel1 is root port. Meaning Po1 leads to a root switch. You don’t enable portfast on a connection connecting two switches and when portfast is not enabled TCN will be set, hence answer D.
Q6 – Actually a TCN BPDU (Not bit) is sent out of Port 1. On subsequent Configuration BPDUs from the Root Bridge the Topology Change bit is set.
Ignore last. it is 802.1w.
Guys, first remember the basics of STP operation and proceed accordingly.
1. ROOT Bridge switch is being elected based on lowest Bridge ID or MAC address
2. Find all root ports next and assign one designated port on the other side of the link.
Criteria is:
Lowest cost to the root switch (from the switch you checking)
Lowest BRIDGE ID from the upstream (sending) switch
Lowest MAC address from the upstream (sending) switch
Lowest port priority ID from upstream (sending) switch
Lowest port ID from the upstream (sending) switch.
3. Then you find blocking ports, according to the same criteria from above, and assign one designated port across.
Q1 – the port on switch SWD that connects to switch SWC (SWC has a lower MAC, therefore its port will be designated, and port on SWD will be blocked) C is correct.
– the port on switch SWB that connects to switch SWD (SWD has a lower cost to the root, therefore his port will be designated, and other side on will be blocked) D is correct.
Q2 – C. The port connecting switch SWC with switch SWE (SWE has a root port to SWC, so traffic will be forwarded)
– D. The port connecting switch SWB with switch SWC (SWB has a root port to SWC, so traffic will be forwarded)